ADME Process: How Your Body Absorbs, Distributes, Metabolizes, and Excretes Medications
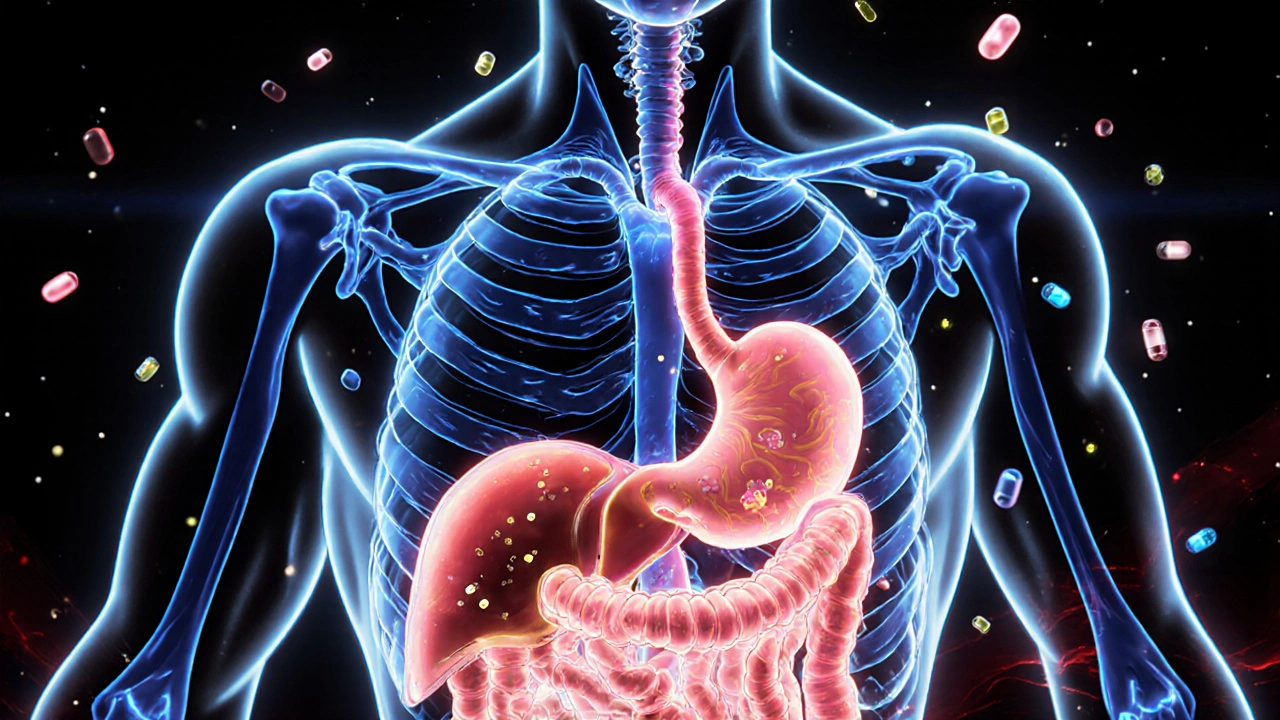
When you take a pill, it doesn’t just disappear and start working. It goes through a hidden journey inside your body called the ADME process, the four-stage biological pathway that determines how a drug moves through and is handled by the body. Also known as absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, it’s the reason why some drugs work fast, others last all day, and some can’t be taken with food or alcohol.
The first step, absorption, how the drug enters your bloodstream, depends on how you take it—swallowed, injected, or applied. A drug taken on an empty stomach might hit your blood faster than one taken with a fatty meal. Then comes distribution, how the drug travels through your body and reaches its target. Some drugs bind to proteins in your blood and can’t reach tissues right away. Others cross the blood-brain barrier, which is why certain meds affect your mood or sleep. Next is metabolism, how your liver breaks down the drug into smaller pieces. This is where interactions happen—like when grapefruit stops your body from processing statins, or St. John’s Wort speeds up the breakdown of antidepressants. Finally, excretion, how your body gets rid of the leftovers, mostly through your kidneys or liver. If your kidneys aren’t working well, even a normal dose can build up to dangerous levels.
Understanding the ADME process isn’t just for doctors or pharmacists. It’s why timing matters when you take your meds—like why some blood pressure pills work best in the morning, or why antibiotics need to be spaced evenly. It explains why generics are safe (they match the brand’s ADME profile) and why some drugs need special monitoring, like those with a narrow therapeutic index. It also shows why certain supplements can mess with your prescriptions. If your body handles a drug differently than expected, it can mean less effect… or more side effects.
Below, you’ll find real-world guides that connect directly to how the ADME process affects your daily health. From how alcohol changes drug metabolism to why bioequivalence studies matter for generics, these posts break down what happens inside you after you swallow a pill—so you know not just what to take, but when, why, and what to watch for.
Pharmacokinetics and Side Effects: How Your Body Processes Drugs
Learn how your body absorbs, breaks down, and removes drugs-and why that affects side effects. From genetics to kidney function, discover the real reasons why medications work differently for different people.